Sometimes it can be hard to grasp the idea that climate change is really happening in 2018, especially when you don’t see its impacts every day. In fact, studies from Yale University show that although most Americans believe that climate change is real, very few believe that it will actually affect them.
Far fewer realize that it actually already is. Here are five ways that climate change is already affecting your life in 2019–and how we’re likely to see them change in the future.
Table of Contents
Extreme Weather and Major Storms are Threatening Our Food Supply
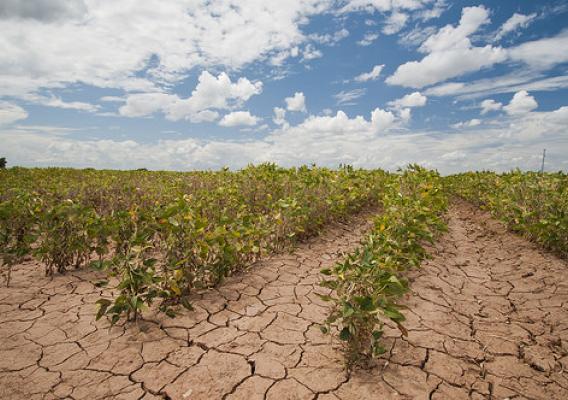 One of the most important impacts of climate change from a human perspective is extreme weather. There has been an increase in the number and scale of weather events, such as hurricanes and tornadoes, hitting the U.S. in the past several years, and all signs point to climate change as the culprit. On top of its potential to destroy entire communities, extreme weather is putting one very important part of our country at risk: our farms.
One of the most important impacts of climate change from a human perspective is extreme weather. There has been an increase in the number and scale of weather events, such as hurricanes and tornadoes, hitting the U.S. in the past several years, and all signs point to climate change as the culprit. On top of its potential to destroy entire communities, extreme weather is putting one very important part of our country at risk: our farms.
Though technology has generally increased short-term crop yields, sunlight, temperature, and precipitation are still the key ingredients for plant growth–and that means that food production still relies heavily on the health of the climate. Extreme weather and altered weather patterns can bring drought, flooding, and fluctuating temperatures, all of which can destroy crops and make them more vulnerable to infection and infestations.
Related
Dying Corals Could Cost Us Billions
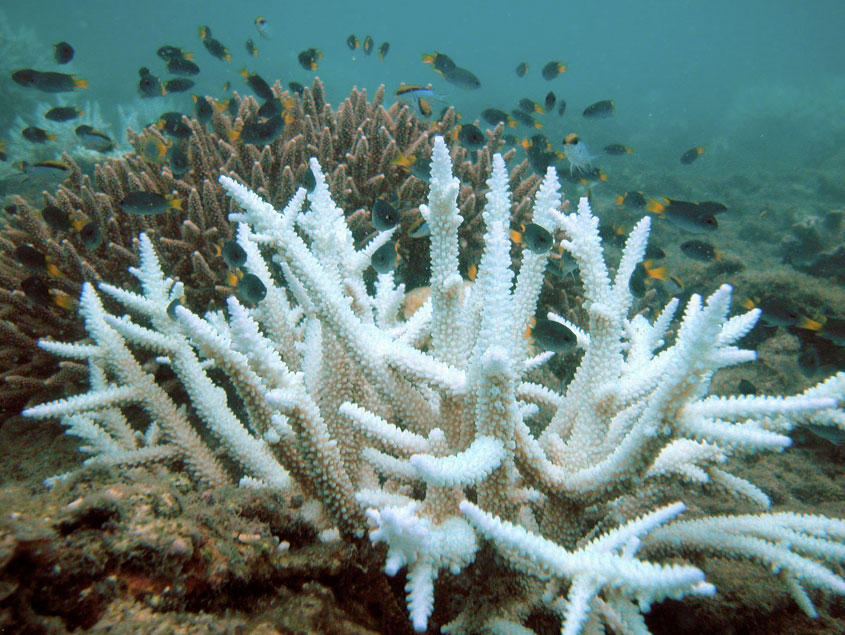 One of the biggest impacts that high temperatures and increasing CO2 levels is having on our planet is taking place under the sea–on coral reefs! More than half of the area that was once covered by corals has been lost over the last 250 years, and much of this is due to climate change.
One of the biggest impacts that high temperatures and increasing CO2 levels is having on our planet is taking place under the sea–on coral reefs! More than half of the area that was once covered by corals has been lost over the last 250 years, and much of this is due to climate change.
Not only are our oceans getting warmer, they’re also becoming more acidic. The world’s oceans naturally absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, leading to a phenomenon called ocean acidification. Since corals are extremely sensitive, ocean acidification and warm waters are causing corals to die off in startling waves of “coral bleaching”.
Aside from the fact that these “underwater rainforests” are a huge attraction due to their beauty and biodiversity, coral reefs are some of the most valuable natural structures on the planet. Because they support so much life, reefs are vital to the global commercial fishing industry. They also act as a natural underwater barrier, protecting coastlines from flooding during storms.
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, losing corals would mean $375 billion in global economic losses every year.
Related
Climate-Induced Heat Waves Are Making You Sick
 Research has shown that that global temperatures are increasing, and days with temperatures above 90 degrees fahrenheit are becoming much more common. And rises in extreme heat can have alarming impacts on human health–particularly, on our lungs. According to National Weather Service data, heat waves have lead to more deaths in the last decade than all other types of weather phenomenon–including hurricanes and tornadoes.
Research has shown that that global temperatures are increasing, and days with temperatures above 90 degrees fahrenheit are becoming much more common. And rises in extreme heat can have alarming impacts on human health–particularly, on our lungs. According to National Weather Service data, heat waves have lead to more deaths in the last decade than all other types of weather phenomenon–including hurricanes and tornadoes.
When temperatures soar, air quality can become extremely poor; sometimes to the point of creating prolonged periods when it is harmful to breathe. That’s because extreme heat and sunlight combine with emissions from cars and other burning fossil fuels to create ground-level ozone–the nasty key ingredient to smog. When inhaled, ozone causes respiratory irritation that is especially dangerous to children, the elderly, and those with asthma.
While this is most common in the southwestern United States, rising temperatures have meant that other areas of the country, such as the Northeast, are seeing an increase in the frequency of days with unhealthy ozone levels. Without preventative measures, this could mean more hospital visits and cases of severe respiratory illnesses throughout the U.S.
Increase in Forest Fires Threatens Air Quality Hundreds of Miles Away
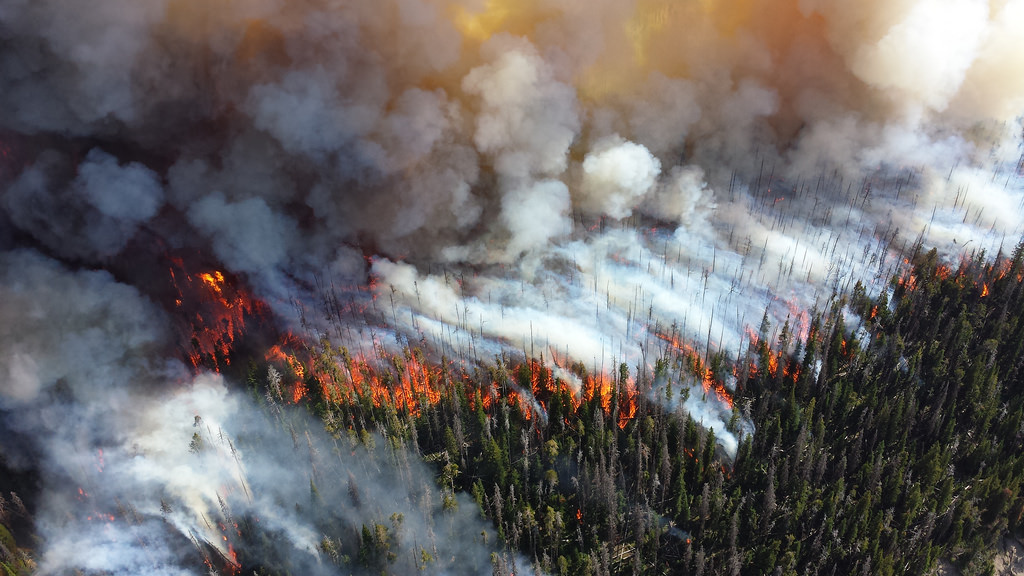 In the past few decades,the frequency of forest fires has increased in the United States. This is largely due to extreme weather events that dry out plant material and make it more prone to burning. With extreme temperatures increasing every year, the number of forest fires is expected to follow a similar trend. It is predicted that by 2050, the season for wildfires will be three weeks longer, burn hundreds of acres of more land, and produce double the amount of smoke.
In the past few decades,the frequency of forest fires has increased in the United States. This is largely due to extreme weather events that dry out plant material and make it more prone to burning. With extreme temperatures increasing every year, the number of forest fires is expected to follow a similar trend. It is predicted that by 2050, the season for wildfires will be three weeks longer, burn hundreds of acres of more land, and produce double the amount of smoke.
While these fires pose a major threat to land and homes in forest fire territory, they threaten much more than that. The smoke produced by forest fires can travel hundreds of miles away–impacting air quality in cities far from where the fire actually happened.
Researchers have predicted that climate change will continue to increase Americans’ exposure to smoke-polluted air, putting millions at risk.
Sea Level Rise Could Cause a Housing Crisis

Photo by GREG COOPER/EPA-EFE/Shutterstock Water floods from Boston Harbor onto Seaport Boulevard at the Boston Fish Pier in the Seaport district of Boston, Massachusetts, USA, 02 March 2018.
There is clear evidence that sea levels are rising. But recent developments have indicated that seas are no longer rising at a steady rate. Instead, sea level rise has begun to accelerate over time. This means that, if the rate of sea level rise continues to change at this pace, the average sea level will be about 2 feet higher by the end of this century. This also means that we’ve underestimated how much rising sea levels could really impact the United States–even for those living far away from coastal areas. Many major US cities, including Boston and Miami, experienced record breaking high tides during this past year; sometimes even on sunny days. These floods are already lowering coastal home valuations–and this trend is is expected to continue as flooding gets worse.
Though this may seem like a distant issue if you live inland, have you ever thought of where the inhabitants of coastal areas will go once their towns are under water? While one option could be rebuilding city infrastructures to combat flooding, this will cost billions of dollars (which we all pay in taxes!) and it may not even solve the issue. The other option is for coastal dwellers to relocate to inland communities–leading to overcrowding and further disruptions to real estate markets.
The impacts of climate change are very important issues to consider, and this is part of the reason why we’re so passionate about our work here at Solstice. Supporting clean energy is just one of the steps that we can take to live more sustainably and help turn climate change around, but it’s one of the biggest, and simplest steps that we can take today!




This is really helpful, thanks.